How expensive is it to dig a septic system, well?
Discover the costs of installing a septic system and well, including tank types, labor, permits, and financing options. Plan your budget effectively.
Installing a septic system and well is essential for homes not connected to municipal utilities. These systems provide water supply and wastewater management but involve significant costs. This guide details the expenses, factors affecting costs, and strategies to manage them.
Septic System Costs
Overview
The cost of a new septic system typically ranges from $3,615 to $12,408, with a national average of around $8,011, according to Angi. Costs vary based on tank material, system type, property size, and additional factors like permits and labor.
Septic Tank Costs by Material
Septic tanks are constructed from various materials, each with distinct advantages and price points:
- Concrete: Durable and common, but prone to cracking. Costs range from $700 to $2,000.
- Fiberglass: Lightweight and resistant to cracking, ideal for shifting soils. Costs range from $1,200 to $2,000.
- Plastic: Affordable but less durable, susceptible to damage. Costs range from $500 to $2,000.
- Steel: Rarely used due to rusting risks, not recommended for new installations.
| Material | Average Cost | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | $700–$2,000 | Durable, long-lasting | Prone to cracking |
| Fiberglass | $1,200–$2,000 | Crack-resistant, lightweight | Higher cost |
| Plastic | $500–$2,000 | Affordable | Easily damaged |
| Steel | Not available | N/A | Rust-prone, hazardous |
Septic System Types
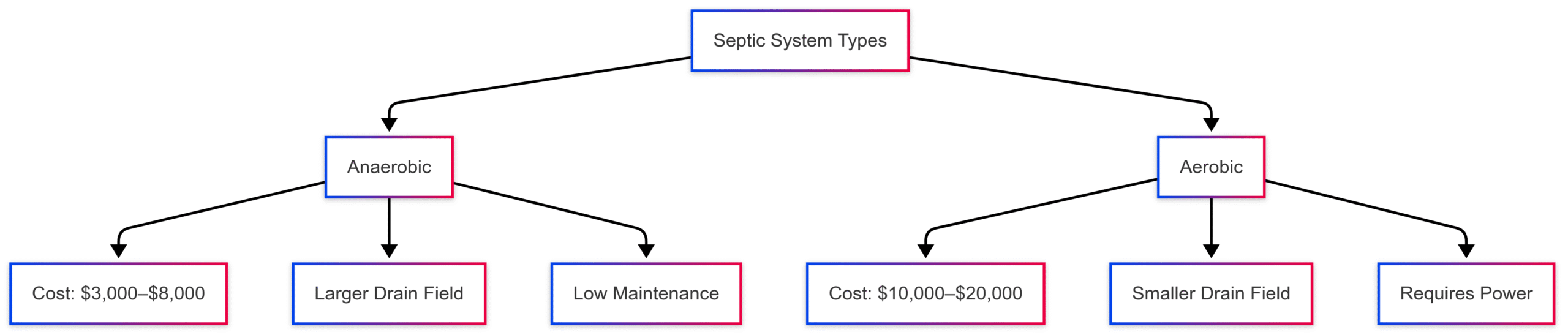
Septic systems are either anaerobic or aerobic, impacting cost and efficiency:
- Anaerobic Systems: Cost $3,000–$8,000. Use gravity and anaerobic bacteria to break down waste. Require larger drain fields, making them less suitable for small lots but more affordable.
- Aerobic Systems: Cost $10,000–$20,000. Use oxygen to enhance bacterial activity, making them more efficient and suitable for smaller properties. Require power and additional maintenance.
Septic Tank Costs by House Size
The size of the septic tank depends on the number of bedrooms, reflecting household wastewater production:
| House Size | Tank Size (Gallons) | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Bedroom | 500 | $500–$900 |
| 2 Bedrooms | 750–1,000 | $700–$1,200 |
| 3–4 Bedrooms | 1,000 | $900–$1,500 |
| 5–6 Bedrooms | 1,200 | $1,200–$1,600 |
| 6–7 Bedrooms | 1,500 | $1,500–$2,500 |
Drain Field Costs
Many septic systems include a drain field (leach field) to disperse wastewater into the soil. Costs depend on tank size and field dimensions:
- 1,000-Gallon Tank: Requires a 600 sq. ft. drain field, costing around $10,240.
- 1,500-Gallon Tank: Requires a 750–1,000 sq. ft. drain field, costing $12,430–$14,370.
Labor Costs
Labor typically accounts for 50% to 70% of total septic system costs, ranging from $1,400 to $4,100. Excavation, if not included, adds $1,500–$6,300.
Additional Septic System Costs
- Design and Engineering Fees: $500–$3,000 for system plans to meet local regulations.
- Percolation Testing: $450–$1,400 to assess soil drainage suitability.
- Permits: $320–$1,880, varying by local requirements.
- Land Surveys: $330–$900 to confirm property boundaries.
- Maintenance Costs:
- Old tank removal: $45–$200 per hour.
- Septic tank pumping: $300–$600 every 3–5 years.
- Pump replacement: $800–$1,400.
- Drain field replacement: $7,000.
Alternative Septic Systems
For properties unsuitable for traditional systems, alternatives include:
| System Type | Average Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Mound | $10,000–$20,000 | High water tables |
| Sand Filter | $7,000–$18,000 | Near water bodies |
| Chamber | $5,000–$12,000 | Variable input (e.g., vacation homes) |
| Drip | $8,000–$18,000 | Shallow soil |
| Evapotranspiration | $10,000–$15,000 | Arid climates |
| Built Wetland | $5,000–$12,000 | Sustainable, eco-friendly |
Well Installation Costs
Overview
Drilling a well costs $3,500–$15,000, depending on depth, type, and materials. Wells provide a private water source, eliminating municipal water bills but requiring maintenance.
Well Costs by Depth
Deeper wells cost more due to increased labor and equipment needs:
| Depth (Feet) | Price Range |
|---|---|
| 50 | $1,775–$3,060 |
| 100 | $3,550–$6,120 |
| 150 | $5,325–$9,180 |
| 200 | $7,100–$12,240 |
| 250 | $8,875–$15,300 |
| 300 | $10,650–$18,360 |
Well Costs by Type
Different well types serve various purposes:
| Well Type | Price per Foot | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Artesian | $25–$85 | $5,000–$15,000 |
| Geothermal | $15–$40 | $3,500–$5,000 |
| Irrigation | $50–$100 | $5,000–$75,000 |
| Residential | $25–$65 | $3,750–$15,300 |
| Sand Point | $10–$25 | $200–$3,000 |
Well Installation Methods
- Digging: $10–$25 per foot, limited to 100 feet.
- Drilling: $15–$100 per foot, suitable for deeper wells.
- Driving: $10–$25 per foot, for shallow wells up to 50 feet.
Well Components and Costs
- Casing Pipe: $630–$2,400 (PVC: $6–$10/foot; Steel: $30–$130/foot).
- Electrical Components: $150–$500 for pump wiring.
- Purification System: $500–$3,000, plus $200–$400 installation.
- Storage Tank: $100–$2,400, depending on size.
- Well Pump: $150–$2,000, with submersible pumps for deep wells costing more.
Additional Well Costs
- Permits: $5–$500.
- Water Testing: $50–$150 (DIY) or $100–$500 (professional).
- Redrilling: $300–$600 for existing wells.
Combined Well and Septic System Costs
For off-grid properties, installing both a well and septic system typically costs $5,000–$22,000. Combining installations can reduce labor costs by sharing trenching and contractor visits.
| Utility Type | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| Well | $3,500–$15,000 |
| Septic | $3,400–$11,500 |
| Combined | $5,000–$22,000 |
Factors Affecting Costs
- Property Size and Layout: Larger homes require bigger tanks and drain fields, increasing costs.
- Soil Conditions: Rocky or clay-heavy soil raises drilling and trenching expenses.
- Distance from Utilities: Longer distances increase piping and wiring costs.
- Geographic Location: Regional variations in labor rates and water table depth affect pricing.
- Permits and Regulations: Local requirements may mandate additional tests or inspections.
Financing Options
- Personal Loans: Suitable for those with good credit, offering lower interest rates.
- Home Equity Loans/Lines of Credit: Use home equity for lower rates, but require sufficient equity.
- Home Equity Investments (HEI): Provide lump-sum cash for a share of future home appreciation, with no monthly payments. Require a minimum credit score of 500 and 15% home equity.
Saving on Installation Costs
- Get Multiple Quotes: Compare at least three quotes from licensed contractors.
- Purchase Materials: Buy materials separately if contractors allow, potentially saving on markups.
- Off-Season Scheduling: Install during low-demand periods for possible discounts.
- Combine Trenching: Share trenches for multiple utilities to reduce labor costs.
- Explore Incentives: Check for state or local rebates and tax incentives.
Maintenance Tips
- Septic System:
- Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items (e.g., wipes, diapers).
- Use septic-safe cleaning products.
- Prevent soil compaction over drain fields by avoiding heavy machinery.
- Pump tank every 3–5 years ($300–$600).
- Well:
- Test water quality annually ($100–$500).
- Maintain pump and electrical components.
- Replace pumps every 10–20 years ($300–$2,000).
Conclusion
Installing a septic system and well is a significant investment, with costs ranging from $5,000 to $22,000 combined. Understanding material choices, system types, and local regulations is crucial for budgeting. By obtaining multiple quotes, exploring financing options, and maintaining systems properly, homeowners can manage expenses effectively.
Why Install a Septic System and Well?
Homes in rural areas or without municipal utility access rely on septic systems and wells for wastewater management and water supply. A septic system treats and disposes of household wastewater, while a well provides a private water source, eliminating municipal water bills. These systems are essential for making a property habitable, but their installation involves complex processes and significant costs.
The Septic System Installation Process
Installing a septic system is not a DIY project due to its complexity and regulatory requirements. The process includes:
- Site Assessment: A percolation test ($450–$1,400) evaluates soil drainage. A land survey ($330–$900) confirms property boundaries.
- Permitting: Obtain permits ($320–$1,880) from local authorities.
- Design: An engineer designs the system ($500–$3,000) to meet local codes.
- Excavation and Installation: Professionals dig the tank site and drain field, install the tank, and connect plumbing ($1,400–$4,100 for labor).
- Inspection: Local authorities inspect the system to ensure compliance.
The Well Installation Process
Well installation also requires professional expertise, especially for residential water supply. The steps include:
- Site Selection: Geological surveys identify water sources. A land survey ensures the site is on your property.
- Permitting: Obtain drilling permits ($5–$500).
- Drilling/Digging: Contractors use drilling ($15–$100/foot), digging ($10–$25/foot), or driving ($10–$25/foot) based on depth and soil.
- Component Installation: Install casing, pump, purification system, and storage tank.
- Water Testing: Professional testing ($100–$500) ensures water safety.
Comparing Septic and Well to Municipal Utilities
Connecting to municipal water and sewer systems costs $2,500–$11,700, often less than installing a well and septic system. However, wells and septic systems eliminate ongoing utility bills, potentially saving $500 annually. They’re ideal for remote properties but require upfront investment and maintenance.
Long-Term Considerations
- Septic System Lifespan: With proper maintenance, septic systems last 20–40 years, with concrete tanks potentially lasting up to 100 years.
- Well Lifespan: Wells can last decades, but pumps and components need replacement every 10–20 years.
- Property Value: A functional well and septic system can increase property value in rural areas, but a failing system may deter buyers.
FAQs
Costs range from $8,000–$20,000, depending on system type, soil conditions, and local regulations.
Standard policies typically don’t cover wear-and-tear replacements but may cover damage from insured events. Check with your insurer.
Labor, accounting for 50%–70% of costs, is typically the most expensive component.
Installation takes 1–7 days, depending on depth, soil conditions, and weather.
For rural properties or those with poor municipal water quality, a well can save on utility bills and increase property value, but consult professionals to assess feasibility.
Conclusion
Installing a septic system and well is a costly but necessary investment for off-grid homes. Costs range from $5,000 to $22,000, influenced by tank materials, system types, property conditions, and labor. By understanding these factors, comparing quotes, and exploring financing options like home equity investments, homeowners can budget effectively. Regular maintenance ensures longevity, reducing the need for costly repairs and maximizing the value of these essential systems.
Please share this How expensive is it to dig a septic system, well? your friends and do a comment below about your feedback.
We will meet you on next article.
Until you can read, Can I use a 15 amp outlet on a 20 amp breaker?






